|
|
|
| Version | Unicode 3.2.0 |
| Authors | Members of the Editorial Committee |
| Date | 2001-12-21 |
| This Version | http://www.unicode.org/unicode/reports/tr28/tr28-1 |
| Previous Version | N/A |
| Latest Version | http://www.unicode.org/unicode/reports/tr28 |
| Tracking Number | x |
This document defines Version 3.2 of the Unicode Standard. This draft is for review with the intention of it becoming a Unicode Standard Annex.
This document has been made available for public review as a Proposed Draft Unicode Technical Report. Publication does not imply endorsement by the Unicode Consortium. This is a draft document which may be updated, replaced, or superseded by other documents at any time. This is not a stable document; it is inappropriate to cite this document as other than a work in progress.
Links to files in the Unicode Character Database will not work at this time. Preliminary versions of these files are available in the beta directory.
A list of current Unicode Technical Reports is found on http://www.unicode.org/unicode/reports/. For more information about versions of the Unicode Standard, see http://www.unicode.org/unicode/standard/versions/.
The References provide related information that is useful in understanding this document. Please mail corrigenda and other comments to the author(s).
Unicode 3.2 is a minor version of the Unicode Standard. It overrides certain features of Unicode 3.1, and adds a significant number of coded characters.
|
The Unicode Consortium. The Unicode Standard, Version 3.2.0 is defined by The Unicode Standard, Version 3.0 (Reading, MA, Addison-Wesley, 2000. ISBN 0-201-61633-5), as amended by the Unicode Standard Annex #27: Unicode 3.1 (http://www.unicode.org/reports/tr27/) and by the Unicode Standard Annex #28: Unicode 3.2 (http://www.unicode.org/reports/tr28/). |
The Unicode Standard, Version 3.2.0 is defined by the following list. The version numbering and the role of each component are explained in Versions of The Unicode Standard. The symbols in the change status column are explained in the key below. A summary of modifications in the Unicode Character Database for this version can be found in UnicodeCharacterDatabase-3.2.0.html, together with a list of which data files contain normative vs. informative data.
N New in this release D Data change (possibly also format/text change) F Data format change (possibly also text change) T Text annotation change - Unchanged
The list of contributory data files constituting the Unicode Standard, Version 3.2 can also be found online at Enumerated Versions.
The primary feature of Unicode 3.2 is the addition of 1016 new encoded characters. These additions consist of several Philippine scripts, a large collection of mathematical symbols, and small sets of other letters and symbols.
All of the newly encoded characters in Unicode 3.2 are additions to the Basic Multilingual Plane (BMP).
Complete introductions to the newly encoded scripts and symbols can be found in Article IV, Block Descriptions, below.
Unicode 3.2 also features amended contributory data files, to bring the data files up to date against the expanded repertoire of characters. A summary of the revisions to the data files can be found in Article VII, Unicode Character Database Changes.
All outstanding errata and corrigenda to the Unicode Standard are included in this specification. Major corrigenda having a bearing on conformance to the standard are listed in Article II, Conformance. Other minor errata are listed in Article VI, Errata.
Most notable among the corrigenda to the standard is a further tightening of the definition of UTF-8, to eliminate irregular UTF-8 and to bring the Unicode specification of UTF-8 more completely into line with other specifications of UTF-8.
The sections of this document are referred to as "articles" to prevent confusion with references to sections of The Unicode Standard, Version 3.0. In addition, the articles in this document are numbered with Roman numerals, to highlight the distinction. The word "section" always refers to sections of The Unicode Standard, Version 3.0. Page numbers also refer to The Unicode Standard, Version 3.0.
New or replacement text for the standard is indicated with underlined text, when this new text is a corrigendum of an existing section of the standard.
Deleted text from the standard is indicated with struck-through
text.
In instances where entire new sections or subsections are to be added to the standard, as for the block descriptions for newly encoded scripts or symbol sets, new section numbers are provided that interleave reasonably with the existing sections of the published Unicode 3.0 book. And for these added sections, the text is not underlined, since the entire sections are new.
In this document, unambiguous dates of the current common era, such as 1999, are unlabeled. In cases of ambiguity, CE is used. Dates before the common era are labeled with BCE.
To reflect the addition of U+2060 WORD JOINER, the conformance rule C10 of Unicode 3.1 is amended as follows:
| C10 |
| C10 | A process shall make no change in a valid coded character representation
other than the following, if that process purports not to modify the
interpretation of that coded character sequence: (a) the possible replacement of character sequences by their canonical-equivalent sequences, or (b) the deletion of noncharacter code points, or (c) the replacement of U+FEFF ZERO WIDTH NO-BREAK SPACE, where not used with signature semantics, by U+2060 WORD JOINER |
The definition of transformation formats such as UTF-8 allowed conformant processes to interpret certain sequences called irregular sequences. These irregular sequences are those that would be produced by transforming supplementary code points as if they were a sequence of two surrogate code points.
To tighten the definitions, in Unicode 3.2 such irregular sequences are now illegal. To still provide for the interpretation of irregular sequences in older implementations of UTF-8, a separate compatibility encoding scheme can be used. See Unicode Draft Technical Report #26, "Compatibility Encoding Scheme for UTF-16: 8-Bit (CESU-8)."
Terminology to distinguish ill-formed, illegal, and irregular code unit sequences is no longer needed. There are no irregular code unit sequences, and thus all ill-formed code unit sequences are illegal. It is illegal to emit or interpret any ill-formed code unit sequence. Unicode 4.0 will revise the terminology and conformance clauses in light of this. For Unicode 3.2, only the minimal changes required of the text are noted here.
Change C12 in Unicode 3.1 to:
| C12 | (a) When a process generates data in a Unicode
Transformation Format, it shall not emit ill-formed code unit sequences. (b) When a process interprets data in a Unicode Transformation Format, it shall treat (c) A conformant process shall not interpret |
Change the fifth note after C12 in Unicode 3.1 to:
Change Table 3.1B after C12 in Unicode 3.1 by splitting the row U+1000..U+FFFF to exclude the surrogate code points:
| Code Points | 1st Byte | 2nd Byte | 3rd Byte | 4th Byte |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| U+0000..U+007F | 00..7F | |||
| U+0080..U+07FF | C2..DF | 80..BF | ||
| U+0800..U+0FFF | E0 | A0..BF | 80..BF | |
| U+1000..U+CFFF | E1..EC | 80..BF | 80..BF | |
| U+D000..U+D7FF | ED | 80..9F | 80..BF | |
| U+D800..U+DFFF | ill-formed | |||
| U+E000..U+FFFF | EE..EF | 80..BF | 80..BF | |
| U+10000..U+3FFFF | F0 | 90..BF | 80..BF | 80..BF |
| U+40000..U+FFFFF | F1..F3 | 80..BF | 80..BF | 80..BF |
| U+100000..U+10FFFF | F4 | 80..8F | 80..BF | 80..BF |
The text of D21 is replaced by the following text:
D21 Compatibility composite: a character whose compatibility decomposition is not identical to its canonical decomposition.
The character U+2060 has been added to the standard to allow unambiguous expression of the word-joining semantics. U+2060 WORD JOINER is now the preferred character to express the word-joining semantics implied by the ZWNBSP. The availability of U+2060 makes it unnecessary to use U+FEFF as a zero-width non-breaking space, allowing U+FEFF to be used solely with the semantic of BOM. For more information, see the subsection on Word Joiner in Section 13.2, Layout Controls in this document.
A number of characters have been added in the Unicode Standard, Version 3.2 which have special character properties. To reflect this, the following changes are made to the special character properties listing, on pages 48-50 of The Unicode Standard, Version 3.0:
In the entry for “Line boundary control", add:
205F MEDIUM MATHEMATICAL SPACE
2060 WORD JOINER
Change the name of the “Joining“ entry to “Cursive joining and ligation control".
Add a new entry called “Grapheme joining“ after the renamed entry for “Cursive joining and ligation control“ and add to that new entry:
034F COMBINING GRAPHEME JOINER
Add a new entry called “Mathematical expression formatting" after the entry “Bidirectional ordering“ and add to that new entry:
2061 FUNCTION APPLICATION
2062 INVISIBLE TIMES
2063 INVISIBLE SEPARATOR
Change the name of the “Alternate formatting“ entry to "Deprecated alternate formatting".
Change the name of the “Indic dead-character formation“ entry to “Brahmi-derived script dead-character formation“ and add to that entry:
1714 TAGALOG SIGN VIRAMA
1734 HANUNOO SIGN PAMUDPOD
Change the name of the “Mongolian variant selectors“ entry to "Mongolian variation selectors".
After the “Mongolian variation selectors“ entry add a new entry “Generic variation selectors“ and add to that new entry:
FE00 VARIATION SELECTOR-1
FE01 VARIATION SELECTOR-2
FE02 VARIATION SELECTOR-3
FE03 VARIATION SELECTOR-4
FE04 VARIATION SELECTOR-5
FE05 VARIATION SELECTOR-6
FE06 VARIATION SELECTOR-7
FE07 VARIATION SELECTOR-8
FE08 VARIATION SELECTOR-9
FE09 VARIATION SELECTOR-10
FE0A VARIATION SELECTOR-11
FE0B VARIATION SELECTOR-12
FE0C VARIATION SELECTOR-13
FE0D VARIATION SELECTOR-14
FE0E VARIATION SELECTOR-15
FE0F VARIATION SELECTOR-16
Hangul Syllables. Where a grapheme cluster contains a Hangul syllable, the combining mark applies to the entire syllable. For example, in the following sequence the grave is applied to the entire Hangul syllable, not just the last jamo:
Enclosing Combining Marks. These marks enclose the entire preceding grapheme cluster. For example, in the following sequence the entire Hangul syllable is circled, not just part of it:
On the other hand, where elements are linked by a Grapheme_Link, non-enclosing combining marks only apply to the last base character. For example, in the following sequence the nukta applies to the immediately preceding ddha, not to the entire cluster:
For more information, see the newly revised Section 5.15, Locating Text Element Boundaries and the subsection on "Combining Grapheme Joiner" in Section 13.2, Layout Controls in this document.
The following text replaces the text and tables for this section on pages 52-3 of The Unicode Standard, Version 3.0.
The Unicode Standard contains both a large set of precomposed modern Hangul syllables and a set of conjoining Hangul jamo, which can be used to encode archaic syllable blocks as well as modern syllable blocks. This section describes how to
For more information, see the "Hangul Syllables" and "Hangul Jamo" subsections in Section 10.4, Hangul in The Unicode Standard, Version 3.0. Hangul syllables are a special case of grapheme clusters. For more information, see the newly revised subsection "Grapheme Cluster Boundaries" in Section 5.15, Locating Text Element Boundaries in this document.
The jamo characters can be classified into three sets of characters: choseong (leading consonants, or syllable-initial characters), jungseong (vowels, or syllable-peak characters), and jongseong (trailing consonants, or syllable-final characters). In the following discussion, these jamo are abbreviated as L (leading consonant), V (vowel), and T (trailing consonant); syllable breaks are shown by middle dots "·"; non-syllable breaks are shown by "×", combining marks are shown by M, and non-jamo are shown by X.
In the following discussion, a syllable refers to a sequence of Korean characters that should be grouped into a single cell for display. This is different from a precomposed Hangul syllable, which consists of any of the characters in the range U+AC00..U+D7A3. Note that a syllable may contain a precomposed Hangul syllable plus other characters.
In rendering, a sequence of jamos is displayed as a series of syllable blocks. The following rules specify how to divide up an arbitrary sequence of jamos (including nonstandard sequences) into these syllable blocks. In these rules, a choseong filler (Lf ) is treated as a choseong character, and a jungseong filler (Vf ) is treated as a jungseong.
The precomposed Hangul syllables are of two types: LV or LVT. In determining the syllable boundaries, the LV behave as if they were a sequence of jamo L V, and the LVT behave as if they were a sequence of jamo L V T.
Within any sequence of characters, a syllable break never occurs between the pairs of characters shown in Table 3-5. In all other cases, there is a syllable break before and after any jamo or precomposed Hangul syllable. Note that like other characters, any combining mark between two conjoining jamos prevents the jamos from forming a syllable.
Table 3-5. Hangul Syllable No-Break Rules
| Don’t Break Between | Examples | |
| L | L, V, or precomposed Hangul syllable |
L × L L× V L × LV L × LVT |
| V or LV | V or T |
V × V V × T LV × V LV × T |
| T or LTV | T | T × T LVT × T |
|
Jamo or precomposed Hangul syllable |
Combining marks | L × M V × M T × M LV × M LVT × M |
Note that even in normalization form NFC, a syllable may contain a precomposed Hangul syllable in the middle. An example is "L LVT T". Each well-formed modern Hangul syllable, however, is of the form L V T? (that is one L, one V and optionally one T), and is a single character in NFC.
For information on the behavior of Hangul compatibility jamo in syllables, see Section 10.4, Hangul in The Unicode Standard, Version 3.0.
A standard Korean syllable block is composed of a sequence of one or more L followed by a sequence of one or more V and optionally a sequence of zero or more T. A sequence of nonstandard syllable blocks can be transformed into a sequence of standard Korean syllable blocks by inserting choseong fillers (Lf ) and jungseong fillers (Vf ).
Using regular expression notation, a standard Korean syllable is thus of the form:
L+ V+ T*
The transformation of a string of text into standard Korean syllables is performed by determining the syllable breaks as explained in the subsection on "Syllable Boundaries" earlier in this section, then inserting one or two fillers as necessary to transform each syllable into a standard Korean syllable. Thus:
L ^V → L Vf ^V
^L V → ^L Lf V
^V T → ^V Lf Vf T
where ^X indicates a character that is not X, or the absence of a character.
Examples. In Table 3-6, the first row shows syllable breaks in a standard sequence, the second row shows syllable breaks in a nonstandard sequence, and the third row shows how the sequence in the second row could be transformed into standard form by inserting fillers into each syllable.
Table 3-6. Syllable Break Examples
|
No. |
Sequence | Sequence with Syllable Breaks Marked | |
|
1 |
LVTLVLVLVfLfVLfVfT |
→ | LVT · LV · LV · LVf · LfV · LfVfT |
|
2 |
LLTTVVTTVVLLVV | → | LL · TT · VVTT · VV · LL · LLVV |
|
3 |
LLTTVVTTVVLLVV | → | LLVf · LfVfTT · LfVVTT · LfVV · LLVf · LLVV |
Replace the subsection on "Grapheme Boundaries" (p. 126-127 in The Unicode Standard, Version 3.0) with the following:
One or more Unicode characters may make up what the user thinks of as a character. To avoid ambiguity with the computer use of the term character, this is called a grapheme cluster. For example, "G" + acute-accent is a grapheme cluster: it is thought of as a single character by users, yet is actually represented by two Unicode characters.
Grapheme clusters include, but are not limited to, combining character sequences such as (g + °), digraphs such as Slovak "ch", or sequences with letter modifiers such as kw. Grapheme cluster boundaries are important for collation, regular-expressions, and counting “character” positions within text. In this section, the Unicode Standard provides a determination of where the default grapheme boundaries fall in a string of characters. This algorithm can be tailored for specific locales or other customizations, which is what is done in providing contracting characters in collation tailoring tables.
Note that default grapheme clusters were previously referred to as "locale-independent graphemes". The term cluster has been added to emphasize that the term grapheme as used differently in linguistics. For simplicity and to align with Unicode Technical Standard #10, "Unicode Collation Algorithm", the terms "locale-independent" and "locale-dependent" been also changed to "default" and "tailored" respectively.
As far as a user is concerned, the underlying representation of text is not important, but it is paramount that an editing interface present a uniform implementation of what the user thinks of as characters. Grapheme clusters should behave as units in terms of mouse selection, arrow key movement, backspacing, and so on. For example, if an accented character is represented by a combining character sequence, then using the right arrow key should normally skip from the start of the base character to the end of the last combining character. In those rare circumstances where end-users need character counts, the counts need to correspond to the grapheme cluster boundaries.
The principal requirements for general character boundaries are the handling of combining marks, Hangul conjoining jamo, and Indic and Tibetan character clusters. See Table 5-3, Grapheme Cluster Boundaries below.
Table 5-3. Grapheme Cluster Boundaries
| CR | Carriage Return |
| LF | Line Feed |
| Join_Control | Join_Control, as determined by the UCD. |
| Link | Grapheme_Link, as determined by the UCD. Includes
most viramas and the grapheme joiner. |
| Extend | Grapheme_Extend, as determined by the UCD. Includes
combining marks. |
| Base | Grapheme_Base, as determined by the UCD. |
| L | Hangul leading jamo U+1100..U+115F (also included in Base) |
| V | Hangul vowel jamo U+1160..U+11A2 (also included in Base) |
| T | Hangul trailing jamo U+11A8..U+11F9 (also included in Base) |
| LV | Precomposed Hangul syllable that is canonically equivalent to a sequence of <L,V> (also included in Base) |
| LVT | Precomposed Hangul syllable that is canonically equivalent to a sequence of <L,V,T> (also included in Base) |
| Any | Any character (includes all of the above) |
|
Do not break between a CR and LF |
|||
| ¬ CR | × | LF | (1) |
|
Do not break between a base character and a combining mark. |
|||
| Base | × | Extend | (2) |
|
Do not break between base characters and link characters, or vice versa. Do not break around a join control if it is preceded by a link and followed by a base. These rules provide for Indic graphemes, where virama will link character clusters together, and join controls can affect the display. |
|||
| Base | × | Link | (3) |
| Link | × | Base | (4) |
| Link | × | Join_Control Base | (5) |
|
Do not break Hangul syllable sequences. |
|||
| L | × | ( L | V | LV | LVT ) | (6) |
| ( LV | V ) | × | ( V | T ) | (7) |
| ( LVT | T) | × | T | (8) |
|
If none of the above are true, break after all characters. |
|||
| Any | ÷ | (9) | |
The only time a grapheme cluster does not begin with a base character is when a combining mark is at the start of text, or preceded by a control or format character. In that case, the control or format character is treated as a grapheme cluster for the purpose of iteration.
The only instance where the boundary cannot be determined by just the adjacent characters is with a Join_Control. The sequence Link, Join_Control, Base does not break, but otherwise there is a grapheme cluster boundary on both sides of a Join_Control.
For more information on the composition of Hangul Syllables (with L, V, or T) see "Hangul Syllables" in the newly revised Section 3.11, Conjoining Jamo Behavior in this document.
Degenerate Cases. As with other definitions in Chapter 5 and
elsewhere, such definitions are designed to be simple to implement. They need to
provide an algorithmic determination of the valid, default grapheme clusters,
and exclude sequences that are normally not considered default grapheme
clusters. However, they do not have to catch edge cases that will not
occur in practice. Mismatched sequences such as <DEVANAGARI KA, HANGUL
JONGSEONG YEORINHIEUH, COMBINING ACUTE> may end up being characterized
as a single default grapheme cluster, but it is not worth the extra
complications in the definition that would be required to catch all of these
cases, because they will not occur in practice.
The definition of a default grapheme clusters is not meant to exclude the use of more sophisticated definitions of tailored grapheme clusters where appropriate: definitions that more precisely match the user expectations within individual languages. For example, "ch" may be considered a grapheme cluster in Slovak. It is, however, designed to provide a much more accurate match to overall user expectations for characters than is provided by individual Unicode code points.
Display of Grapheme Clusters. Grapheme clusters are not the same as ligatures. For example, the grapheme cluster "ch" in Slovak is not normally a ligature, and conversely, the ligature "fi" is not normally a grapheme cluster. Default grapheme clusters do not necessarily reflect text display. For example, the sequence <f, i> may be displayed as a single glyph on the screen, but would still be two grapheme clusters.
For more information on the use of grapheme clusters, see Unicode Technical Report #18, "Unicode Regular Expression Guidelines".
Note: The numbering used here for block descriptions and revised text follows The Unicode Standard, Version 3.0 for ease of cross-reference.
Invisible Operators. In mathematics some operators or punctuation are often implied, but not displayed. U+2063 INVISIBLE SEPARATOR or invisible comma is intended for use in index expressions and other mathematical notation where two adjacent variables form a list and are not implicitly multiplied. In mathematical notation, commas are not always explicitly present, but need to be indicated for symbolic calculation software to help it disambiguate a sequence from a multiplication. For example, the double ij subscript in the variable aij means ai, j — that is, the i and j are separate indices and not a single variable with the name ij or even the product of i and j. Accordingly to represent the implied list separation in the subscript ij one can insert a nondisplaying invisible separator between the i and the j. In addition, use of the invisible comma would hint to a math layout program to typeset a small space between the variables.
Similarly an expression like mc2 implies that the mass m multiplies the square of the speed c. To represent the implied multiplication in mc2, one inserts a nondisplaying U+2061 INVISIBLE TIMES between the m and the c. A related case is the use of U+2062 FUNCTION APPLICATION for an implied function dependence as in f(x + y). To indicate that this is the function f of the quantity x + y and not the expression fx + fy, one can insert the nondisplaying function application symbol between the f and the left parenthesis.
Another example is the expression f ij(cos(ab)), which means the same as fij(cos(a×b)), where × represents multiplication, not the cross product. Note that the spacing between characters may also depend on whether the adjacent variables are part of a list or are to be concatenated, that is, multiplied.
A more complete discussion of mathematical notation can be found in Proposed Draft Unicode Technical Report #25, “Unicode Support for Mathematics."
Commercial Minus. U+2052 COMMERCIAL MINUS SIGN is used in commercial or tax related forms or publications in several European countries, including Germany and Scandinavia. The string "./." appears to be used as a fallback representation for this character.
The symbol may also appear as a marginal note in letters, denoting enclosures. One variation replaces the top dot with a digit indicating the number of enclosures.
An additional usage of the sign appears in the Finno-Ugric Phonetic
Alphabet (FUPA), where it marks a structurally-related borrowed element of
different pronunciation. In Finland, the dingbats
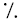 and
and
 are used for “correct” and “incorrect” respectively
in marking a student’s paper. This contrasts
with American practice, for example, where
are used for “correct” and “incorrect” respectively
in marking a student’s paper. This contrasts
with American practice, for example, where  and
and 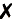 can be used for “correct” and “incorrect”
respectively in the same context.
can be used for “correct” and “incorrect”
respectively in the same context.
On p. 155 of The Unicode Standard, Version 3.0 update the first full paragraph as follows:
This block encodes punctuation marks and symbols primarily used by writing systems that employ Han ideographs. Most of these characters are found in East Asian standards.
U+3008, U+3009 angle brackets are unambiguously wide. The Unicode Standard encodes different characters for use in other contexts, such as mathematics. There are other characters in this block that have the same characteristics, including double angle brackets, tortoise shell brackets, and white square brackets.
With Unicode 3.0 and the concurrent second edition of ISO/IEC 10646-1, the reference glyphs for U+03C6 GREEK LETTER SMALL PHI and U+03D5 GREEK PHI SYMBOL were swapped. In ordinary Greek text, the character U+03C6 is used exclusively, although this characters has considerably glyphic variation, sometimes represented with a glyph more like the representative glyph shown for U+03C6 (the "loopy" form) and less often with a glyph more like the representative glyph shown for U+03D5 (the “straight“ form).
For mathematical and technical use, the straight form of the small phi is an important symbol and needs to be consistently distinguishable from the loopy form. The straight form phi glyph is used as the representative glyph for the symbol phi at U+03D5 to satisfy this distinction.
The reversed assignment of representative glyphs in versions of the Unicode Standard prior to Unicode 3.0 had the problem that the character explicitly identified as the mathematical symbol did not have the straight form of the character that is the preferred glyph for that use. Furthermore, it made it unnecessarily difficult for general purpose fonts supporting ordinary Greek text to also add support for Greek letters used as mathematical symbols. This resulted from the fact that many of those fonts already used the loopy form glyph for U+03C6, as preferred for Greek body text; to support the phi symbol as well, they would have had to disrupt glyph choices already optimized for Greek text.
When mapping symbol sets or SGML entities to the Unicode Standard, it is important to make sure that codes or entities that require the straight form of the phi symbol be mapped to U+03D5 and not to U+03C6. Mapping to the latter should be reserved for codes or entities that represent the small phi as used in ordinary Greek text.
Fonts used primarily for Greek text may use either glyph form for U+03C6, but fonts that also intend to support technical use of the Greek letters should use the loopy form to ensure appropriate contrast with the straight form used for U+03D5.
The first of these four scripts, Tagalog, is no longer used, although the other three, Hanunóo, Buhid, and Tagbanwa, are living scripts of the Philippines. South Indian scripts of the Pallava dynasty made their way to the Philippines, although the exact route is uncertain. They may have been transported by way of the Kavi scripts of Western Java between the 10th and 14th centuries CE.
There are written accounts of the Tagalog script by Spanish missionaries, and documents in Tagalog dating from the mid-1500s. The first book in this script was printed in Manila in 1593. While the Tagalog script was used to write Tagalog, Bisaya, Ilocano, and other languages, it fell out of normal use by the mid-1700s; modern Tagalog language is now written in the Latin script.
The three living scripts, Hanunóo, Buhid, and Tagbanwa, are related to Tagalog, but may not be directly descended from it. The Hanunóo and the Buhid peoples live in Mindorom while the Tagbanwa live in Palawan. Hanunóo enjoys the most use; it is widely used to write love poetry, a popular pastime among the Hanunóo. Tagbanwa is less used.
The Philippine scripts share features with the other Brahmi-derived scripts to which they are related.
Consonant Letters. Philippine scripts have consonants containing an inherent -a vowel, which may be modified by the addition of vowel signs or canceled (killed) by the use of a virama-type mark.
Independent Vowel Letters. Philippine scripts have null consonants which are used to write syllables that start with a vowel.
Dependent Vowel Signs. The vowel -i is written with a mark above the associated consonant, and the vowel -u with an identical mark below. The mark is known in Tagalog as kudlit "diacritic," tuldik "accent," or tildok "dot," and ulitan "diacritic" in Tagbanwa. The Philippine scripts employ only the two vowel signs i and u, which are also used to stand for the vowels e and o respectively.
Virama. Though all languages normally written with the Philippine scripts have syllables ending in consonants, not all of the scripts have a mechanism for expressing the
canceled -a. As a result, in those orthographies, the final consonants are unexpressed. Francisco Lopez introduced a cross-shaped
virama in his 1620 catechism in the Ilocano language, but this innovation did not seem to find favor with native users, who seem to have considered the script adequate without it (they preferred
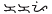 kakapi to
kakapi to 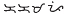 kakampi). A similar reform for the Hanunóo script seems to have been better received. The Hanunóo
pamudpod was devised by Antoon Postma, who went to the Philippines from the Netherlands in the mid-1950s. In traditional orthography,
kakampi). A similar reform for the Hanunóo script seems to have been better received. The Hanunóo
pamudpod was devised by Antoon Postma, who went to the Philippines from the Netherlands in the mid-1950s. In traditional orthography,
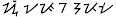 si apu ba upada is, with the
pamudpod, rendered more accurately as
si apu ba upada is, with the
pamudpod, rendered more accurately as 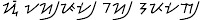 si aypud bay upadan; the Hanunóo pronunciation is
si aypod bay upadan. The Tagalog virama and Hanunóo pamudpod cancel only the inherent
-a. No conjunct consonants are employed in the Philippine scripts.
si aypud bay upadan; the Hanunóo pronunciation is
si aypod bay upadan. The Tagalog virama and Hanunóo pamudpod cancel only the inherent
-a. No conjunct consonants are employed in the Philippine scripts.
Directionality. The Philippine scripts are read from left to right in horizontal lines running from top to bottom. They may be written or carved either in that manner, or in vertical lines running from bottom to top, moving from left to right. In the latter case, the letters are written sideways so they may be read horizontally. This method of writing is probably due to the medium and writing implements used. Text is often scratched with a sharp instrument onto beaten strips of bamboo which are held pointing away from the body and worked from the proximal to distal ends, in columns from left to right.
Rendering. In Tagalog and Tagbanwa, the vowel signs simply rest over or under the consonants. In Hanunóo and Buhid, however, special ligatures are often formed as shown in the following tables.
|
Hanunóo |
Buhid |
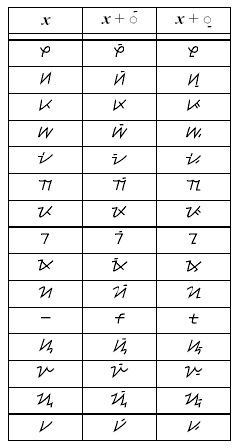 |
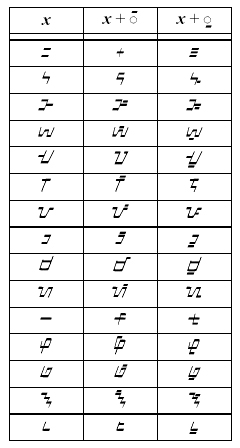 |
Punctuation. Punctuation has been unified for the Philippine scripts. In the Hanunóo block, U+1735 PHILIPPINE SINGLE PUNCTUATION and U+1736 PHILIPPINE DOUBLE PUNCTUATION are encoded. Tagalog makes use only of the latter; Hanunóo, Buhid, and Tagbanwa make use of both of them.
Unicode 3.2 adds 59 new ideographs to the Compatibility Ideographs block. These new compatibility ideographs are found from U+FA30 to U+FA6A. They are included in the Unicode Standard to provide full round-trip compatibility with the ideographic repertoire of JIS X 0213:2000 and should not be used for any other purpose.
Katakana Phonetic Extensions: U+31F0..U+31FF
These extensions to the Katakana syllabary are all “small“ variants. They are used in Japan for phonetic transcription of Ainu and other languages.
When Hangul compatibility jamo are transformed with a compatibility normalization form, NFKD or NFKC, the characters are converted to the corresponding conjoining jamo characters. Where the characters are intended to remain in separate syllables after such transformation, they may require separation from adjacent characters. This can be done by inserting any non-Korean character.
For example, the table below illustrates how two Hangul compatibility jamo can be separated in display, even after transforming with NFKD or NFKC.
| Original |
NFKD |
NFKC |
Display | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||
|
|
|
|
Like Arabic letters, Mongolian letters have various presentation forms depending on their positions in words. There are additional linguistic constraints that result in variations that must be employed in specific contexts, creating the need for several Mongolian-specific variant selectors, which are encoded at U+180B, U+180C, and U+180D.
The table of standardized variants in the Unicode Character Database found at http://www.unicode.org/Public/3.2-Update/StandardizedVariants-3.2.0.html provides a description of the variant appearances corresponding to the use of appropriate variation selectors with all allowed base Mongolian characters. Only some presentation forms of the base Mongolian characters used with the Mongolian free variation selectors produce variant appearances. These combinations are exhaustively listed and described in the table. All combinations not listed in the table are unspecified and are reserved for future standardization; no conformant process may interpret them as standardized variants.
For more information, see Section 13.7, Variation Selectors, later in this document.
In addition to the symbols in these blocks, mathematical and scientific notation makes frequent use of arrows, punctuation characters, letterlike symbols, geometrical shapes and other miscellaneous and technical symbols. For additional information on all the mathematical operators and other symbols, see Proposed Draft Unicode Technical Report #25, “Unicode Support for Mathematics."
Other symbols used in mathematical and scientific notation can be found in the Geometric Shapes block. For an extensive discussion of mathematical alphanumeric symbols, see Section 12.2, Letterlike Symbols in The Unicode Standard, Version 3.0. For additional information on all the mathematical operators and other symbols, see Proposed Draft Unicode Technical Report #25, “Unicode Support for Mathematics."
The Unicode Standard defines a number of additional blocks to supplement the repertoire of mathematical operators and arrows. These additions are intended to extend the Unicode repertoire sufficiently to cover the needs of such applications as MathML, modern mathematical formula editing and presentation software, and symbolic algebra systems.
Standards. MathML, an XML application, is intended to support the full legacy collection of the ISO mathematical entity sets. Accordingly, the repertoire of mathematical symbols for the Unicode Standard has been supplemented by the full list of mathematical entity sets in ISO TR 9573-13, Public entity sets for mathematics and science. Additional repertoire was provided from the amalgamated collection of the STIX Project (Scientific and Technical Information Exchange). That collection includes, but is not limited to, symbols gleaned from mathematical publications by experts of the American Mathematical Society and symbol sets provided by Elsevier Publishing and by the American Physics Society.
Semantics. The same mathematical symbol may have different meanings in different subdisciplines or different contexts. The Unicode Standard only encodes a single character for a single symbolic form. For example, the “+“ symbol normally denotes addition in a mathematical context, but might refer to concatenation in a computer science context dealing with strings, or incrementation, or have any number of other functions in given contexts. It is up to the application to distinguish such meanings according to the appropriate context. Where information is available about the usage (or usages) of particular symbols, it has been indicated in the character annotations in Chapter 14, Code Charts in The Unicode Standard, Version 3.0.
This block contains many additional symbols to supplement the collection of mathematical operators.
This block contains symbols used mostly as operators or delimiters in mathematical notation.
Mathematical Brackets. The mathematical white square brackets, angle brackets, and double angle brackets encoded at U+27E6..U+27EB are intended for ordinary mathematical use of these particular bracket types. They are unambiguously narrow, for use in mathematical and scientific notation, and should be distinguished from the corresponding wide forms of white square brackets, angle brackets, and double angle brackets used in CJK typography. (See the CJK Symbols and Punctuation block.) Note especially that the “bra“ and “ket“ angle brackets, U+2329 LEFT-POINTING ANGLE BRACKET and U+232A RIGHT-POINTING ANGLE BRACKET, are now deprecated for use with mathematics because of their canonical equivalence to CJK angle brackets, which is likely to result in unintended spacing problems if used in mathematical formulae.
This block contains miscellaneous symbols used for mathematical notation, including fences and other delimiters. Some of the symbols in this block may also be used as operators in some contexts.
Wiggly Fence. U+29DB LEFT WIGGLY FENCE has a superficial similarity to U+FE34 PRESENTATION FORM FOR VERTICAL LOW LINE. The latter is a wiggly sidebar character, intended for legacy support as an style of underlining character in a vertical text layout context; it has a compatibility mapping to U+005F LOW LINE. This represents a very different usage from the standard use of fence characters in mathematical notation.
This block contains a small additional set of arrows to supplement the main set in the Arrows block.
Long Arrows. The long arrows encoded in the range U+27F5..U+27FF map to standard SGML entity sets supported by MathML. Long arrows represent distinct semantics from their short counterparts, rather than mere stylistic glyph differences. For example, the shorter forms of arrows are often used in connection with limits, whereas the longer ones are associated with mappings. The use of the long arrows is so common that they were assigned entity names in the ISOAMSA entity set, one of the suite of mathematical symbol entity sets covered by the Unicode Standard.
This block contains a large additional repertoire of arrows to round out the main set in the Arrows block.
Keytop Labels. [to precede "Crops and Quine Corners"] Where possible, keytop labels have been unified with other symbols of like appearance, for example U+21E7 UPWARDS WHITE ARROW to indicate the shift key. While symbols such as U+2318 PLACE OF INTEREST SIGN and U+2388 HELM SYMBOL are generic symbols that have been adapted to use on keytops, other symbols specifically follow ISO/IEC 9995-7.
Angle Brackets. [to follow "Crops and Quine Corners"] U+2329 LEFT-POINTING ANGLE BRACKET and U+232A RIGHT-POINTING ANGLE BRACKET have long been canonically equivalent to the CJK punctuation characters, U+3008 LEFT ANGLE BRACKET and U+3009 RIGHT ANGLE BRACKET, respectively. This canonical equivalence implies that the use of the latter (CJK) code points is preferred, and that U+2329 and U+232A are also “wide“ characters. (See Unicode Standard Annex #11, "East Asian Width", for the definition of the East Asian wide property.) Because of this fact, the use of U+2329 and U+232A is deprecated for mathematics and technical publication, where the wide property of the characters has the potential for interfering with proper formatting of mathematical formulae. Instead, use the angle brackets specifically provided for mathematics: U+27E8 MATHEMATICAL LEFT ANGLE BRACKET and U+27E9 MATHEMATICAL RIGHT ANGLE BRACKET. See Section 12.4, Mathematical Operators earlier in this document.
Symbol Pieces. [to follow "APL Functional Symbols"] The characters in the range U+239B..U+23B3, plus U+23B7, comprise a set of bracket and other symbol fragments for use in mathematical typesetting. These pieces originated in older font standards, but have been used in past mathematical processing as characters in their own right to make up extra-tall glyphs for enclosing multi-line mathematical formulae. Mathematical fences are ordinarily sized to the content that they enclose. However, in creating a large fence, the glyph is not scaled proportionally; in particular the displayed stem weights must remain compatible with the accompanying smaller characters. Thus, simple scaling of font outlines cannot be used to create tall brackets. Instead, a common technique is to build up the symbol from pieces. In particular, the characters U+239B LEFT PARENTHESIS UPPER HOOK through U+23B3 SUMMATION BOTTOM represent a set of glyph pieces for building up large versions of the fences (, ), [, ], {, and }, and of the large operators ∑ and ∫. These brace and operator pieces are compatibility characters. They should not be used in stored mathematical text, but are often used in the data stream created by display and print drivers.
The following table shows which pieces are intended to be used together to create specific symbols.
Use of Symbol Pieces
|
|
2-row |
3-row |
5-row |
|
Summation |
23B2, 23B3 |
|
|
|
Integral |
2320, 2321 |
2320, 23AE, 2321 |
2320, 3×23AE, 2321 |
|
Left Parenthesis |
239B, 239D |
239B, 239D |
239B, 3×239C, 239D |
|
Right Parenthesis |
239E, 23A0 |
239E, 239F, 23A0 |
239E, 3×239F, 23A0 |
|
Left Bracket |
23A1, 23A3 |
23A1, 23A2, 23A4 |
23A1, 3×23A2, 23A3 |
|
Right Bracket |
23A4, 23A6 |
23A4, 23A5, 23A6 |
23A4, 3×23A5, 23A6 |
|
Left Brace |
23B0, 23B1 |
23A7, 23A8, 2389 |
23A7, 23AA, 23A8, 23AA, 2389 |
|
Right Brace |
23B1, 23B0 |
23AB, 23AC, 23AD |
23AB, 23AA, 23AC, 23AA, 23AD |
For example, an instance of U+239B can be positioned relative to instances of U+239C and U+2390 to form an extra-tall (three or more line) left parenthesis. The center sections encoded here are meant to be used only with the top and bottom pieces encoded adjacent to them because the segments are usually graphically constructed within the fonts so that they match perfectly when positioned at the same x coordinates.
Vertical Square Brackets. The vertical square brackets, U+23B4 TOP SQUARE BRACKET and U+23B5 BOTTOM SQUARE BRACKET, are compatibility characters for legacy applications emulating certain terminals. They are intended for those terminal applications only, for limited use in vertically-oriented bracketed expressions. U+23B6 BOTTOM SQUARE BRACKET OVER TOP SQUARE BRACKET is used when a single character cell is both the end of one such expression and the start of another. These compatibility characters should not be confused with the general need for rotated glyphs for parentheses, brackets, braces, and quotation marks for vertically rendered CJK text. Such rotations should be handled by fonts and rendering software, rather than by separate encoding of each rotated glyph as a character. See further discussion in Section 6.1, General Punctuation in The Unicode Standard, Version 3.0.
Terminal Graphics Characters. In addition to the box-drawing characters in the Box Drawing block, a small number of additional vertical or horizontal line characters are encoded in the Miscellaneous Technical symbols block to complete the set of compatibility characters needed for applications which need to emulate various old terminals. The horizontal scan line characters, U+23BA HORIZONTAL SCAN LINE-1 through U+23BD HORIZONTAL SCAN LINE-9, in particular, represent characters that were encoded in character ROM for use with 9-line character graphic cells. Horizontal scan line characters are encoded for scan lines 1, 3, 7, and 9. The horizontal scan line character for scan line 5 is unified with U+2500 BOX DRAWINGS LIGHT HORIZONTAL.
Dental Symbols. The set of symbols from U+23BE to U+23CC form a set of symbols from JIS X0213 for use in dental notation.
Standards. This block contains a large number of symbols from ISO/IEC 9995-7:1994 “Information technology -- Keyboard layouts for text and office systems -- Part 7: Symbols used to represent functions".Plastic Bottle Material Code System. The seven numbered logos encoded from U+2673 to
U+2679  are from “The Plastic Bottle Material Code System,” introduced in 1988 by the Society of the Plastics Industry (SPI) (see
http://www.socplas.org). This set consistently uses thin, two-dimensional curved arrows suitable for use in plastics molding. In actual use, the symbols often are combined with an abbreviation of the material class below the triangle. Such abbreviations are not universal, therefore they are not present in the reference glyphs in Chapter 14, Code Charts.
are from “The Plastic Bottle Material Code System,” introduced in 1988 by the Society of the Plastics Industry (SPI) (see
http://www.socplas.org). This set consistently uses thin, two-dimensional curved arrows suitable for use in plastics molding. In actual use, the symbols often are combined with an abbreviation of the material class below the triangle. Such abbreviations are not universal, therefore they are not present in the reference glyphs in Chapter 14, Code Charts.
Recycling Symbol for Generic Materials. An unnumbered plastic resin code symbol
U+267A ![]() RECYCLING SYMBOL FOR GENERIC MATERIALS is not formally part of the SPI system, but is found in many fonts. Occasional use of this symbol as a generic materials code symbol can be found in the field, usually with a text legend below, but sometimes also surrounding (or overlaid by) other text or symbols.
Sometimes, the UNIVERSAL RECYCLING SYMBOL is substituted for the generic symbol in this
context.
RECYCLING SYMBOL FOR GENERIC MATERIALS is not formally part of the SPI system, but is found in many fonts. Occasional use of this symbol as a generic materials code symbol can be found in the field, usually with a text legend below, but sometimes also surrounding (or overlaid by) other text or symbols.
Sometimes, the UNIVERSAL RECYCLING SYMBOL is substituted for the generic symbol in this
context.
Universal Recycling Symbol. Unicode encodes two common glyph variants of this symbol, U+2672 ![]() UNIVERSAL RECYCLING SYMBOL and U+267B
UNIVERSAL RECYCLING SYMBOL and U+267B ![]() BLACK UNIVERSAL RECYCLING SYMBOL. Both are used to indicate that the material is recyclable. The white form is the traditional version of the symbol, but the black form is sometimes substituted, presumably because the thin outlines of the white form do not always reproduce well.
BLACK UNIVERSAL RECYCLING SYMBOL. Both are used to indicate that the material is recyclable. The white form is the traditional version of the symbol, but the black form is sometimes substituted, presumably because the thin outlines of the white form do not always reproduce well.
Paper Recycling Symbols. The two paper recycling symbols U+267C ![]() RECYCLED PAPER SYMBOL and U+267D
RECYCLED PAPER SYMBOL and U+267D ![]() PARTIALLY-RECYCLED PAPER SYMBOL can be used to distinguish fully and partially recycled fiber content in paper products or packaging. They are usually accompanied by additional text.
PARTIALLY-RECYCLED PAPER SYMBOL can be used to distinguish fully and partially recycled fiber content in paper products or packaging. They are usually accompanied by additional text.
The following text replaces the text on Dingbats on pages 305-306 of The Unicode Standard, Version 3.0:
The Dingbats are derived from a well-established set of glyphs, the ITC Zapf Dingbats series 100, which comprises the industry standard “Zapf Dingbat“ font currently available in most laser printers. Other series of dingbat glyphs also exist, but are not encoded in the Unicode Standard because they are not widely implemented in existing hardware and software as character-encoded fonts. The order of the Dingbats block basically follows the PostScript encoding.
Unifications. Where a dingbat from the ITC Zapf Dingbats series 100 could be unified with a generic symbol widely used in other contexts, only the generic symbol was encoded. This accounts for the encoding gaps in the Dingbats block. Examples of such unifications include card suits, BLACK STAR, BLACK TELEPHONE, and BLACK RIGHT-POINTING INDEX (see "Miscellaneous Symbols"); BLACK CIRCLE and BLACK SQUARE (see "Geometric Shapes"); white encircled numbers 1 to 10 (see “Enclosed Alphanumerics"); and several generic arrows (see “Arrows"). Those four entries appear elsewhere in this section.
In other instances, additional of the ITC Zapf Dingbats series 100 glyphs have come to be recognized as having applicability as generic symbols, despite having originally been encoded in the Dingbats block. For example, the series of negative (black) circled numbers 1 to 10 are now treated as generic symbols for this sequence, the continuation of which can be found in “Enclosed Alphanumerics". Other examples include U+2708 AIRPLANE and U+2709 ENVELOPE, which have definite semantics independent of the specific glyph shape, and which therefore should be considered generic symbols, rather than as symbols representing only the Zapf Dingbat glyph shapes.
For many of the remaining characters in the Dingbat block, their semantic value is primarily their shape; unlike characters that represent letters from a script, there is no well-established range of typeface variations for a dingbat that will retain its identity and therefore its semantics. It would be incorrect to arbitrarily replace U+279D TRIANGLE-HEADED RIGHTWARDS ARROW with any other right arrow dingbat or with any of the generic arrows from the Arrows block (U+2190..U+21FF). But exact shape retention for the glyphs is not always required in order to maintain the relevant distinctions. For example, ornamental characters such as U+2741 EIGHT PETALLED OUTLINE BLACK FLORETTE have been successfully implemented in font faces other than Zapf Dingbats with glyph shapes which are similar, but not identical to the ITC Zapf Dingbats series 100.
The following guidelines are provided for font developers wishing to support this block of characters. Characters showing large sets of contrastive glyph shapes in the Dingbats block, and in particular the various arrow shapes at U+2794..U+27BE, should have glyphs that are closely modeled on the ITC Zapf Dingbats series 100, which are shown as reference glyphs in the code charts. The same applies to the various stars, asterisks, and snowflakes, drop-shadowed squares, checkmarks, and x's, many of which are ornamental, and have an elaborate name describing their glyph.
Where the above does not apply, or where dingbats have more generic applicability as a symbol, their glyphs do not need not to match the reference glyphs in the code charts in every detail.
Ornamental Brackets. The 14 ornamental brackets encoded at U+2768..U+2775 are a late addition to the set of Zapf Dingbats encoded in the Unicode Standard. Although they have always been included in Zapf Dingbats fonts, they were unencoded in PostScript versions of the fonts on some platforms, and hence were omitted from the original set encoded in Unicode. They have been added for compatibility and consistency in handling of the cmaps for current versions of the fonts.
These mathematical variants are all produced with the addition of Variation Selector 1 (VS1 or U+FE00) to mathematical operator base characters. Only the valid, recognized combinations are listed in the table of standardized variants. All combinations not listed here are unspecified and are reserved for future standardization; no conformant process may interpret them as standardized variants.
For more information, see Section 13.7, Variation Selectors, later in this document.
The Combining Grapheme Joiner is used to indicate that adjacent characters belong to the same grapheme cluster. Grapheme clusters are sequences of one or more encoded characters that correspond to what users think of as characters. They include, but are not limited to, combining character sequences such as (g + °), digraphs such as Slovak “ch", or sequences with letter modifiers such as kw. Grapheme cluster boundaries are important for collation, regular-expressions, and counting "character" positions within text. The Unicode Standard provides a determination of where the default grapheme boundaries fall in a string of characters. This algorithm can be tailored for specific locales. For more information, see Section 5.15, Locating Text Element Boundaries, Section 2.7 Special Character and Noncharacter Values, Section 3.8 Transformations, and Section 13.6, Specials in The Unicode Standard, Version 3.0.
There are circumstances where even the locale-specific determination of grapheme boundaries may need to be further tailored on a local basis. These include:
The character U+034F COMBINING GRAPHEME JOINER has been added to prevent inappropriate grapheme breaks. The properties of this character are specified so as to work well with current software for such processes as grapheme-cluster determination, line-break, and collation. In terms of grapheme determination it functions like the Indic viramas. As with a virama, the grapheme joiner is only useful if immediately followed by a base character, so it should always be placed at the end of a combining character sequence. Thus a sequence functions as a single grapheme.
The grapheme joiner prevents line breaking between adjacent characters; however, where this is the only desired effect, the word joiner should be used instead (see Unicode Standard Annex #14, “Line Breaking Properties"). In collation, the grapheme joiner should be ignored unless it specifically occurs within a tailored collation element mapping. Thus it is given a completely ignorable collation element in the default collation table, like NULL (see Unicode Technical Standard #10, " Unicode Collation Algorithm" and also ISO/IEC 14651). However, it can be entered into the tailoring rules for any given language, using the UCA and ISO/IEC 14651 tailoring capabilities.
For rendering, the grapheme joiner is an invisible combining character with canonical class of zero. It binds adjacent characters into a single grapheme as the base for combining marks, such as an underbar in “th". For any specified repertoire, implementation support for this capability can be provided by means of ligature tables in the font, or by means of special placement rules (see http://partners.adobe.com/asn/developer/opentype/main.htm). Some display engines may be able to supply runtime generative support. As with other combining marks, there is considerable latitude for display depending on the environment (such as the choice of font). Some possibilities are:
In Unicode 3.1.1 and before, the codepoint U+FEFF serves two very different purposes:
If U+FEFF had only the semantic of a signature codepoint, it could be freely deleted from text without affecting the interpretation of the rest of the text. Carelessly appending files together, for example, can result in a signature codepoint in the middle of text. Unfortunately, U+FEFF also has significance as a character. As a ZWNBSP, it indicates that line breaks are not allowed between the adjoining characters. Thus U+FEFF impacts the interpretation of text, and cannot be freely deleted. The overloading of semantics for this codepoint has caused problems for programs and protocols.
The new character U+2060 WORD JOINER has the same semantics in all cases as U+FEFF, except that it cannot be used as a signature. That is, the function of the character is to indicate that the two adjacent characters should not be broken across lines. See the GL category in Unicode Standard Annex #14, “Line Breaking Properties". In other contexts the character should be ignored.
Unicode 3.2 implementations should support this new character, but also support the ZWNBSP semantic of U+FEFF.
It is the task of the rendering system to select a ligature (where ligatures are possible) as part of the task of creating the most pleasing line layout. Fonts that provide more ligatures give the rendering system more options.
However, defining the locations where ligatures are possible cannot be done by the rendering system, because there are many languages in which this depends not on simple letter pair context but on the meaning of the word in question.
ZWJ and ZWNJ are to be used for the latter task, marking the non-regular cases where ligatures are required or prohibited. This is different from selecting a degree of ligation for stylistic reasons. Such selection is best done with style markup. See Unicode Technical Report #20, "Unicode in XML and other Markup Languages" for more information.
The need arises occasionally in text processing to refer to one variant shape of a particular Unicode character. Sometimes, two variants will need to be expressed side-by-side in the same document in plain-text contexts where it is impossible or inconvenient to exchange proprietary text formats. Especially in languages employing the Mongolian script, sometimes a specific variant glyph is needed for a specific textual purpose for which a "generic substitute" glyph is considered inappropriate. At the same time, however, the identity of the glyph is generally acknowledged as one of two or more possible variants of the same underlying character. In this regard such variants form a slightly gray area between characters and glyphs.
The variation selector only selects a different appearance of an already encoded character. It is not to be used as a general code extension mechanism. Only the sequences specifically defined in this annex are sanctioned for standard use; all other sequences are undefined. Each sequence consists of a pair: a base character followed by the variation selector. The base character is never a combining character or a composite character. The variation selectors are combining marks of combining class 0 and have no visible glyphs.
The tables of standardized variants are listed in the Unicode Character
Database in the file:
http://www.unicode.org/Public/UNIDATA/StandardizedVariants.html
The following code charts contain the characters added in Unicode 3.2. They are shown together with the characters that were part of Unicode 3.1. New characters are shown on a yellow background in these code charts.
Code Charts Notice:
Annotations for many characters have been added or revised throughout the code charts. These are not mentioned explicitly in the list above. Please see http://www.unicode.org/charts for a list of all code charts.
This article contains errata rolled up since the publication of The Unicode Standard, Version 3.1. These errata are listed by date in the table below.
| Date | Summary |
|---|---|
| 2001 September 25 | The character U+0B83 TAMIL SIGN VISARGA is actually a stand-alone
character, not a combining character. This character's General Category
has been changed from “Mc“ to “Lo“ in accordance with this. The glyph on
the left below shows the character in previous charts; the glyph on the
right shows the character as it should appear (without a dotted circle).
|
| 2001 April 25 | On p. 500, in the Unicode names list in TUS 3.0, the glyph for U+2032 was omitted. It is shown correctly in the code chart on page 498. It is also shown correctly in the online code charts. |
The main change to the Unicode Character Database for Unicode 3.2 is the extension of the data files to cover the character repertoire addition. This most importantly impacts UnicodeData.txt, LineBreak.txt, and EastAsianWidth.txt, each of which has been extended to cover all the newly encoded characters. Also, an updated informative NamesList.txt file is provided to cover the new repertoire.
Property and Property Value Aliases. The PropertyAliases and PropertyValueAliases files contain contain recommended UCD property identifiers and property value identifiers. These identifers can be used for XML formats of UCD data, for regular-expression property tests, and other programmatic textual descriptions of Unicode data. In comparing identifiers, case differences should not be significant, and the presence or absence of an underbar should be ignored. The identifiers in the PropertyAliases and PropertyValueAliases files are normative in the following sense:
Where the identifiers are used to refer to Unicode properties or property values, they can only be used in accordance with the Unicode Character Database semantics.
This does not prevent implementations from using other identifiers to refer to Unicode property or property values. For example, there is nothing to prevent the use of French translations of the identifiers.
Blocks. The normative blocks defined in Blocks.txt have been adjusted slightly, in accordance with Unicode Technical Committee decisions.
The block property values are listed in the Blocks datafile, and are not repeated in the PropertyValueAliases datafile. (Block property values should be used with caution; for more information see Unicode Technical Report #18, "Unicode Regular Expression Guidelines", Annex A.)
The notes for SpecialCasing.txt have been updated, and the rules for casing involving dotted letters (i, j) have been reformulated more generically.
An updated Index.txt has been provided, to make it easier to locate the newly added characters, particularly for mathematics.
The following new property files have been added:
Other new properties include:
Note: For consistency with the property naming conventions, the property BidiMirrored has been renamed to Bidi_Mirrored (see DerivedBinaryProperties.txt). Also the property Comp_Ex has been renamed to Full_Composition_Exclusion (see DerivedNormalizationProperties.txt).
The documentation files for the Unicode Character Database have been updated to reflect the additions of new property files and new character properties to existing files.
ISO/IEC 10646 is a multi-part standard. Part 1, published as ISO/IEC 10646-1:2000(E), covers the Architecture and Basic Multilingual Plane. Part 2, published as ISO/IEC 10646-2:2001(E), covers the supplementary planes. Amendment 1 to Part 1 makes a few modifications to the architecture of 10646 and adds about a thousand characters to the BMP.
Unicode 3.2 adds all of the characters of Amendment 1, except for the two characters of Amendment 1 that were already added to Unicode 3.1. With the publication of Amendment 1 to ISO/IEC 10646-1:2000 and the Unicode Standard, Version 3.2, the two standards are fully synchronized.
The Unicode Consortium and ISO/IEC JTC1/SC2/WG2 are committed to maintaining the synchronization between the two standards.
Notable among the architectural changes to ISO/IEC 10646 approved in Amendment 1 are:
ISO/IEC 9573-13: International Organization for Standardization. Information technology--SGML support facilities--Techniques for using SGML--Part 13: Public entity sets for mathematics and science. [Geneva], 1991. (ISO/IEC TR 9573-13:1991).
ISO/IEC 9995-7: Information technology--Keyboard layouts for text and office systems--Part 7: Symbols used to represent functions. [Geneva], 1994. (ISO/IEC 9995-7:1994).
ISO/IEC 14651: International Organization for Standardization. Information technology–International string ordering and comparison–Method for comparing character strings and description of the common template tailorable ordering. [Geneva], 2001. (ISO/IEC 14651:2001).
JIS X 0213: Japanese Industrial Standards Committee. 7 bitto oyobi 8 bitto no 2 baito jouhou koukan you fugouka kakuchou kanji shuugou (7-bit and 8-bit double byte coded extended KANJI sets for information interchange). Tokyo, 2000. (JIS X 0213:2000).
Kuipers, Joel C., and Ray McDermott. 1996. “Insular Southeast Asian Scripts”, in Peter T. Daniels and William Bright, eds. The World’s Writing Systems. New York; Oxford: Oxford University Press. ISBN 0-19-507993-0
Santos, Hector. 1994. The Tagalog Script. (Ancient Philippine Scripts Series; 1). Los Angeles: Sushi Dog Graphics.
Santos, Hector. 1995. The Living Scripts. (Ancient Philippine Scripts Series; 2). Los Angeles: Sushi Dog Graphics.
STIPUB Consortium. STIX (Scientific and Technical Information Exchange)
Project.
http://www.ams.org/STIX/
Wolf, Edwin, II, ed. 1947. Doctrina christiana: the first book printed in the Philippines, Manila 1593. A facsimile of the copy in the Lessing J. Rosenwald Collection. Washington, DC: Library of Congress.
The following summarizes modifications from the previous version of this document. Modifications to this document will be limited to repairing straightforward typographical and production errors. Updates in content will be carried out via a future version of the Unicode Standard, published in a separate document.
| T# |
|
Copyright © 2001 Unicode, Inc. All Rights Reserved. The Unicode Consortium makes no expressed or implied warranty of any kind, and assumes no liability for errors or omissions. No liability is assumed for incidental and consequential damages in connection with or arising out of the use of the information or programs contained or accompanying this technical report.
Unicode and the Unicode logo are trademarks of Unicode, Inc., and are registered in some jurisdictions.